The Enigmatic Patch Resistor: Unveiling its Hidden Power
Title: The Enigmatic Patch Resistor: Unveiling its Hidden Power
Introduction:
In the vast realm of electronics, there exists a small yet pivotal component known as the patch Resistor. Found in countless electronic devices, this unassuming component provides vital functionality and plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and efficiency of the circuitry. However, what truly makes the patch Resistor unique is its characteristic of being color-coded, offering a cryptic language that only the initiated can decipher. In this article, we will delve into the world of patch resistors and explore how their colors hold the key to understanding their resistance values.
Unraveling the Mystery:
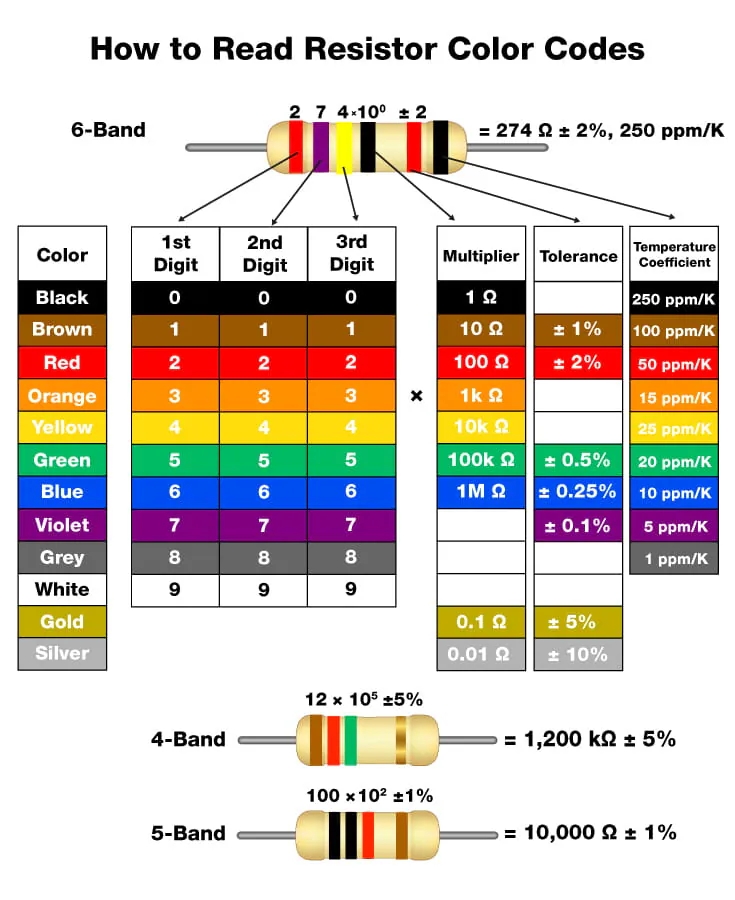
Patch resistors come in a wide spectrum of colors, each hue holding a specific meaning that corresponds to a particular resistance value. As novices in the field of electronics, it is essential to familiarize oneself with this color code, as a wrong choice could prove disastrous for a circuit's functionality.
Black: The color black signifies the lowest resistance value, often in the range of 0-9 ohms. These resistors are commonly used when high currents are required.
Brown: With a resistance range of 10-99 ohms, brown patch resistors offer slightly higher resistance while maintaining their stability. They are widely used in a variety of applications, from household appliances to automotive systems.
Red: The vibrant red-colored patch resistors fall within the resistance range of 100-999 ohms. Their purpose is mainly to moderate current flow in circuits, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
Orange: Patch resistors in captivating orange hues denote resistance values within the range of 1k ohms to 9.9k ohms. These components find their application in voltage dividers, temperature sensors, and precision circuits.
Yellow: With a higher resistance range of 10k ohms to 99k ohms, yellow patch resistors are often used in amplifiers, filters, and other signal processing applications. Their distinctive color acts as a visual cue for experienced engineers.
Green: The color green encompasses the resistance range of 100k ohms to 999k ohms. These resistors are useful in industries such as telecommunications,audio equipment, and power supplies, where precise resistance values are crucial for optimal performance.
Blue: Blue patch resistors have a resistance range of 1M ohm to 9.9M ohms. Used in precision measurement devices, audio amplifiers, and scientific instruments, these resistors ensure accurate and reliable results.
Violet: With a resistance range of 10M ohms to 99M ohms, violet patch resistors are indispensable in high-precision applications such as medical equipment, aerospace technology, and research laboratories.
Grey: Grey patch resistors indicate resistance values within the range of 100M ohms to 999M ohms. These components find their usage in highly specialized circuits that require extremely high resistance levels.
The Color Code Advantage:
The color-coded system of patch resistors offers a convenient and efficient method for engineers and technicians to identify resistance values quickly. By simply looking at the color band combination, professionals can select and integrate the appropriate resistor into their circuits, ensuring accurate and reliable electronic performance.
Conclusion:
The patch resistor, with its color-coded mystery, provides a fascinating glimpse into the intricate world of electronics. Its ability to convey vital resistance information through colors enables engineers and technicians to optimize circuit designs and ensure seamless functionality. As we continue to immerse ourselves in the advancements of technology, let us appreciate the humble patch resistor for its hidden power and the simplicity it adds to the complexity of electronic systems.